Introduction
In an era dominated by environmental concerns and the need for sustainable energy sources, the spotlight has increasingly toward How Does Solar Energy Work? Harnessing the seemingly boundless energy of the sun, solar power has emerged as a key player in the quest for clean and renewable energy. In this blog, we will delve into the intricacies of solar energy, exploring the technology that makes it possible and its potential impact on our planet.
The Basics of Solar Energy
At its core, solar energy is the radiant light and heat from the sun that is harnessed using a range of technologies. The sun releases an astonishing amount of energy, and capturing even a fraction of this power can provide a substantial and sustainable energy source. To understand how solar energy works, it’s essential to explore the key components and processes involved.
Photovoltaic (PV) Cells
Central to the solar energy conversion process are photovoltaic cells, commonly known as solar cells. These cells are made of semiconductor materials, often silicon, and are responsible for converting sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight strikes the surface of these cells, electrons are set into motion, creating an electric current.
The Photovoltaic Effect
The photovoltaic effect is a phenomenon where certain materials generate an electric current when exposed to light. In the context of solar cells, photons, which are particles of light, strike the surface of the PV cells and transfer their energy to the electrons in the semiconductor material. This energy excites the electrons, allowing them to flow and generate an electric current.
Solar Panels and Arrays
Solar cells are grouped to form solar panels, and these panels are then connected to create solar arrays. The combined output from these arrays produces a usable amount of electricity. The efficiency of solar panels has significantly improved over the years, making solar energy an increasingly viable and cost-effective option for generating power.
The Role of Inverters
While solar panels generate direct current (DC) electricity, most household appliances and the power grid operate on alternating current (AC). Inverters play a crucial role in the solar energy system by converting the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity, making it compatible with the electrical systems in homes and businesses.
Net Metering and Grid Connection
One of the significant advantages of energy is the potential to produce more electricity than needed. In a grid-connected solar system, excess electricity can be fed back into the grid, and users may receive credits or compensation for the surplus power they contribute.

This process, known as net metering, encourages the widespread adoption of solar energy and promotes a more sustainable energy ecosystem.
Environmental Benefits of Solar Energy
The adoption of solar energy brings about numerous environmental benefits. Unlike fossil fuels, solar power generation produces minimal greenhouse gas emissions, contributing significantly to the reduction of air pollution and mitigating the impact of climate change. Additionally, solar energy reduces dependence on finite and environmentally harmful resources, such as coal and oil.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While the potential of solar energy is immense, challenges such as intermittent energy production (due to weather conditions and daytime-only availability) and the environmental impact of solar panel manufacturing and disposal need to be addressed. Ongoing research and technological advancements aim to enhance the efficiency of solar cells, reduce costs, and improve the overall sustainability of solar energy.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Solar energy is often touted for its positive impact on both the environment and the economy. By harnessing the power of the sun, we can significantly reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, resulting in a range of environmental benefits.
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions
One of the primary advantages of solar energy is its minimal environmental impact. Unlike traditional fossil fuels, solar power generation produces negligible greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to efforts to mitigate climate change and reduce air pollution.
Job Creation and Economic Growth
The solar industry has experienced rapid growth in recent years, creating jobs and stimulating economic development. From manufacturing and installation to research and development, the solar sector offers diverse employment opportunities while contributing to the overall economic well-being.
Energy Storage Solutions
Enhancing the efficiency of energy storage systems is crucial for addressing the intermittency of solar power. Researchers are exploring new materials and technologies to improve the capacity, durability, and cost-effectiveness of batteries, making solar energy a more reliable and viable source.
Technological Innovations
Ongoing research and development in the field of solar energy are bringing about groundbreaking innovations. From next-generation solar panels with increased efficiency to novel materials that enhance energy capture, the future of solar energy holds the promise of even greater sustainability and affordability.
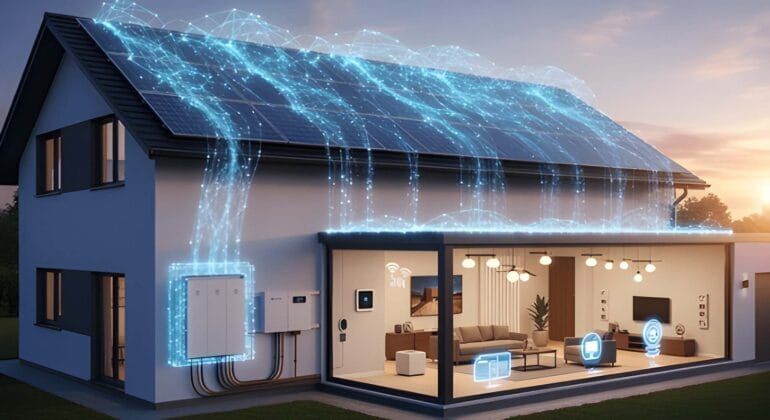
Energy Grid Integration
Integrating solar energy into existing energy grids poses a technical challenge. Fluctuations in energy production due to weather conditions and the intermittent nature of sunlight can strain traditional grids. Smart grid technologies, energy storage solutions, and improved grid management practices are being developed to address these challenges and ensure a seamless integration of solar power into the broader energy infrastructure.
Solar Technology Beyond Electricity Generation
Solar energy’s potential extends beyond traditional electricity generation. Advances in solar thermal technologies are enabling the direct harnessing of solar heat for industrial processes, space heating, and even desalination. By diversifying the applications of solar technology, we can maximize its impact across various sectors.
Conclusion
In the quest for a cleaner and more sustainable future, solar energy stands out as a beacon of hope. Understanding how solar energy works sheds light on the transformative power of harnessing the sun’s rays to generate electricity. As technology continues to evolve, solar energy is poised to play an increasingly pivotal role in meeting the world’s growing energy needs while minimizing environmental impact. Embracing solar power is not just a technological choice; it’s a commitment to a greener, more sustainable planet for generations to come.