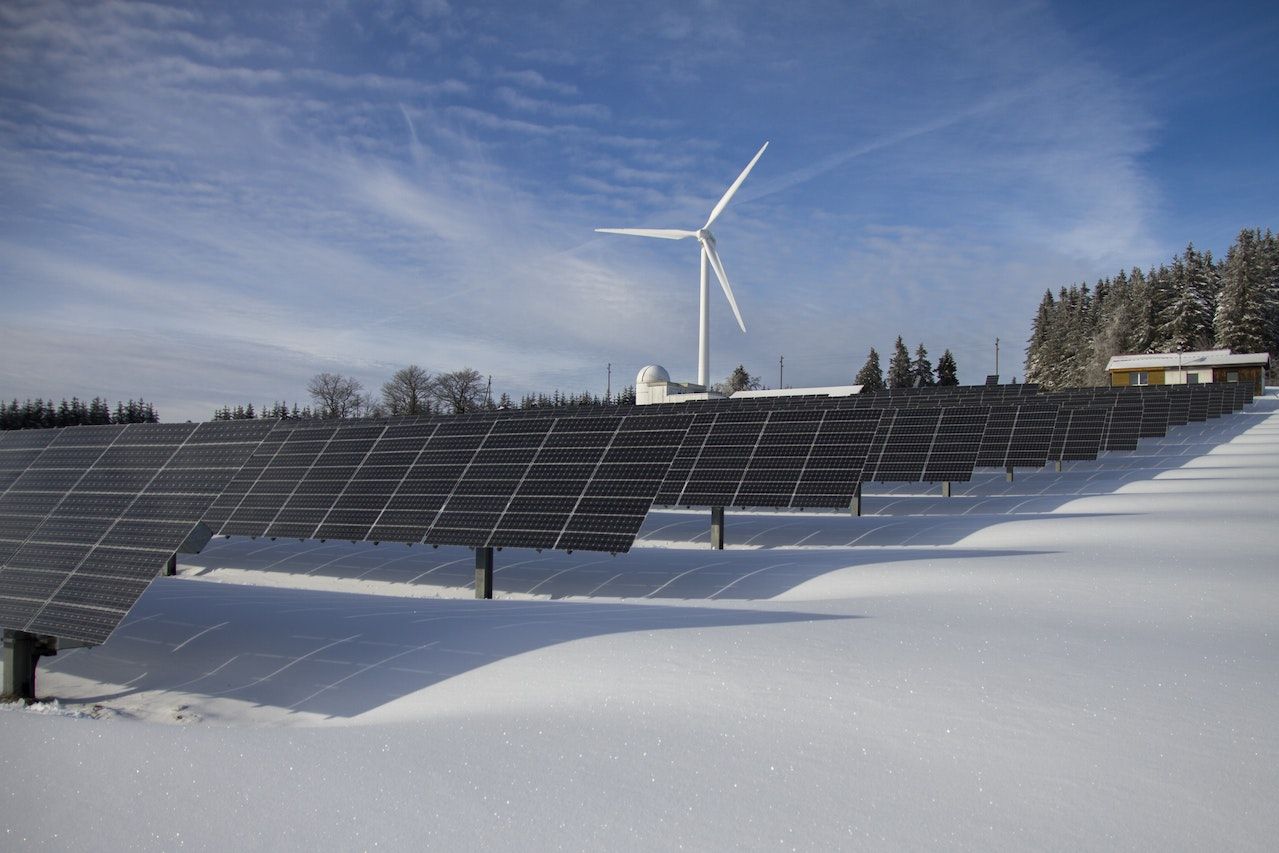
In recent years, the world has witnessed a growing wind and solar concern over the sustainability of traditional energy sources. As climate change becomes an ever more pressing issue, the need to transition to renewable energy has become paramount. Among the various renewable energy options available, wind and solar power have emerged as frontrunners in shaping the future of energy. This article delves into the potential of wind and solar energy, exploring their benefits, challenges, and their role in revolutionizing the global energy landscape.
1. Understanding Wind Energy
1.1 How Wind Energy Works
Wind energy harnesses the power of the wind through wind turbines. As the wind blows, it spins the turbine’s blades, converting the kinetic energy into mechanical energy. This mechanical energy is then transformed into electricity through a generator. Wind farms, comprising multiple turbines, have become a common sight in various regions, producing clean and sustainable energy.
1.2 Advantages of Wind Energy
Wind energy offers numerous advantages. Firstly, it is a renewable and abundant resource, making it highly sustainable. Unlike fossil fuels, wind energy does not emit greenhouse gases, reducing the carbon footprint and combating climate change. Additionally, wind farms can be established both onshore and offshore, providing flexibility in location choices.
1.3 Challenges of Wind Energy
Despite its merits, wind energy faces some challenges. One significant challenge is the intermittency of wind. Wind patterns are unpredictable, leading to fluctuations in energy generation. Additionally, the visual impact of wind turbines in scenic landscapes has raised concerns among some communities.
2. Embracing Solar Power
2.1 Harnessing Solar Energy
Solar power involves capturing the sun’s rays and converting them into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) cells or solar panels. These panels contain semiconductors that release electrons when exposed to sunlight, generating direct current (DC) electricity. This DC electricity is then converted into alternating current (AC) electricity through an inverter, ready for consumption.
2.2 Advantages of Solar Energy
Solar energy presents several advantages. Firstly, it is an inexhaustible source of energy, with the sun expected to shine for billions of years. Solar power systems can be installed on rooftops, making it feasible for decentralized power generation. Moreover, solar panels operate silently and require minimal maintenance, making them cost-effective in the long run.
2.3 Challenges of Solar Energy
Despite its potential, solar energy faces some challenges. One significant obstacle is its dependence on sunlight. Cloudy days and nighttime reduce solar energy production. The cost of installing solar panels can also be a barrier for some consumers, although prices have been decreasing in recent years.
3. The Synergy of Wind and Solar Power
3.1 Complementary Nature
Wind and solar power complement each other exceptionally well. Wind energy often peaks during the winter months when sunlight is scarce, while solar energy production peaks during the summer when wind speeds are comparatively lower. Integrating these two renewable sources can create a more stable and consistent energy supply.
3.2 Hybrid Systems
Hybrid systems that combine wind and solar power have gained popularity. By incorporating battery storage technology, excess energy can be stored when production exceeds demand and utilized during times of low production. This integration enhances energy grid stability and resilience.
4. The Global Impact
4.1 Addressing Climate Change
The adoption of wind and solar energy is crucial in combating climate change. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, these renewable alternatives can significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions and help limit global temperature rise.
4.2 Energy Independence
Promoting wind and solar power fosters energy independence for countries. Relying on domestic renewable resources reduces vulnerability to fluctuations in fossil fuel prices and geopolitical tensions.
5. The Rise of Renewable Energy
5.1 Embracing Sustainable Solutions
As the detrimental impact of fossil fuels becomes increasingly evident, countries worldwide are pivoting towards renewable energy to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change. Wind and solar energy have gained traction due to their abundant availability, low carbon footprint, and potential to replace traditional, polluting energy sources.
5.2 Addressing Energy Security
Wind and solar energy offer greater energy security by reducing reliance on finite resources such as coal, oil, and natural gas. As these conventional sources deplete, renewable energy emerges as a reliable alternative, ensuring a stable and self-sustained energy future.
6. Harnessing the Power of Wind
6.1 The Wind Energy Potential
Wind energy harnesses the kinetic energy from natural wind patterns and converts it into electricity. With advancements in technology and the installation of wind farms, wind energy has become a crucial player in the renewable energy landscape.
6.2 Advantages of Wind Energy
Clean and Green: Wind energy production does not emit greenhouse gases or pollutants, contributing to a cleaner environment.
Renewable Resource: Wind is an infinite resource, making wind energy a sustainable option for meeting our energy demands.
Cost-Effectiveness: Once established, wind farms have lower operational costs compared to fossil fuel power plants.
6.3 Overcoming Challenges
Intermittency: wind is not constant, and energy production depends on wind availability. To address this, energy storage solutions and smart grids are being developed. Land and Wildlife Impact: Large-scale wind farms can have an impact on local ecosystems and wildlife migration patterns, requiring careful planning and consideration.
7. The Promise of Solar Energy
7.1 The Solar Energy Revolution
Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun through photovoltaic cells or solar thermal systems. The proliferation of solar panels on rooftops and solar farms has revolutionized the renewable energy sector.
7.2 Advantages of Solar Energy
Abundant and Accessible: Sunlight is virtually limitless and available in most regions, making solar energy accessible globally.
Zero Emissions: Solar energy production does not emit greenhouse gases, making it an eco-friendly choice.
Reduced Electricity Bills: Solar panel users can save on electricity costs and even sell excess power back to the grid.
7.3 Addressing Limitations
Intermittency: Similar to wind energy, solar energy production is affected by weather conditions, necessitating energy storage solutions.
Initial Costs: The installation of solar panels involves initial expenses, although the long-term savings offset this investment.
8. Converging Paths: Wind and Solar Integration
8.1 Complementary Nature
Wind and solar energy complement each other remarkably well. Solar energy production is often at its peak during the day, while wind energy tends to be more prominent during the night. This complementary relationship ensures a more consistent supply of renewable energy.
8.2 Hybrid Systems
The integration of wind and solar energy in hybrid systems further enhances reliability and efficiency. Hybrid systems enable the use of diverse energy sources to meet varying energy demands, reducing the dependence on non-renewable options.
8.3 Technological Advancements
Ongoing research and development in renewable energy technologies are pivotal to overcoming current limitations. Breakthroughs in energy storage, smart grids, and efficient conversion systems are making wind and solar energy more viable than ever.
8.4 Policy and Investment
Supportive policies and financial incentives play a crucial role in accelerating the adoption of renewable energy. Governments worldwide must foster an environment that encourages investment in wind and solar projects.
9. Challenges in the Adoption of Wind and Solar Energy
While the future of wind and solar energy appears promising, several challenges hinder their rapid adoption.
Some of the challenges include:
Intermittency: Wind and solar energy production depends on weather conditions, making it intermittent and unpredictable.
Energy Storage: Developing efficient and cost-effective energy storage solutions remains a challenge to ensure a steady power supply.
Infrastructure: The establishment of wind and solar farms requires significant initial investments and suitable locations.
10. Wind and Solar in Residential Applications: Powering Homes Sustainably
Wind and solar energy are not limited to large-scale power plants; they are also making their way into residential settings. Homeowners now have the opportunity to generate their electricity, contributing to a cleaner and greener environment while reducing their energy bills.
10.1 Benefits of residential wind and solar systems include:
Lower electricity bills, especially over the long term, as homeowners generate their electricity.
Potential incentives and tax credits offered by governments to promote residential renewable energy adoption. Increased energy independence, reducing reliance on traditional utility providers.
11. Wind and Solar in Transportation: Driving Towards a Greener Future
Beyond electricity generation, wind and solar energy play a vital role in transforming transportation.
Some applications include:
Electric Vehicles (EVs): Solar panels can charge EV batteries, reducing reliance on traditional fuel sources.
Solar-Powered Boats: Solar panels can generate electricity to power boats, reducing emissions in water bodies.
Sustainable Aviation: Researchers are exploring solar-powered aircraft designs to reduce aviation’s carbon footprint.
12. The Future of Wind and Solar Energy: Towards a Renewable Revolution
The future of wind and solar energy is undeniably bright, with their potential to revolutionize the global energy landscape.
Key developments to anticipate:
Technological Innovations: Continued advancements will improve the efficiency and affordability of wind and solar systems.
Grid Integration: Improved grid infrastructure will enable the seamless integration of renewable energy sources.
Energy Storage Solutions: Breakthroughs in storage technologies will address the intermittency challenge.
Conclusion
Wind and solar energy stand as pillars of hope in the quest for a sustainable and greener future. Their potential to reduce carbon emissions, provide clean and renewable energy, and foster energy independence makes them indispensable components of the world’s energy mix.
FAQs
1. Are wind and solar energy entirely emission-free?
Both wind and solar energy are considered almost emission-free during the operation phase. While the manufacturing process and transportation of equipment might have some emissions, they are significantly lower compared to fossil fuel-based power plants.
2. What is the lifespan of solar panels and wind turbines?
Solar panels typically have a lifespan of 25-30 years, while well-maintained wind turbines can last for over 20 years.
3. Can wind and solar energy replace fossil fuels entirely?
While wind and solar energy have tremendous potential, a complete replacement of fossil fuels would require a comprehensive energy strategy that includes energy storage, grid enhancements, and continued research and development.
4. What role do governments play in promoting renewable energy?
Governments play a crucial role in incentivizing and supporting the adoption of renewable energy through policies, subsidies, and regulatory measures.
5. How can individuals contribute to the growth of renewable energy?
Individuals can support renewable energy by adopting energy-efficient practices, investing in rooftop solar installations, and advocating for renewable energy policies in their communities.