Heat pumps are a type of heating and cooling system that have gained popularity in recent years. They work by transferring heat from one location to another, rather than generating heat like traditional heating systems or like Solar thermal technology. Heat pumps are more energy-efficient than traditional heating systems, making them an eco-friendly option that can also save you money on your energy bills.
Types of Heat Pumps
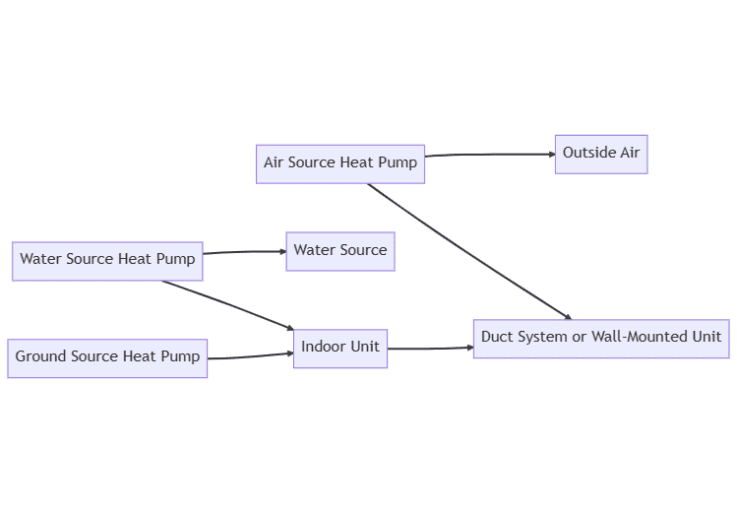
There are three main types of heat pumps: air source, ground source, and water source. Air source are the most common type and are easy to install.
Ground source are more expensive to install but can be more efficient in certain conditions. Water source are the most efficient type of heat pump but can also be the most expensive.
Air Source Heat Pumps
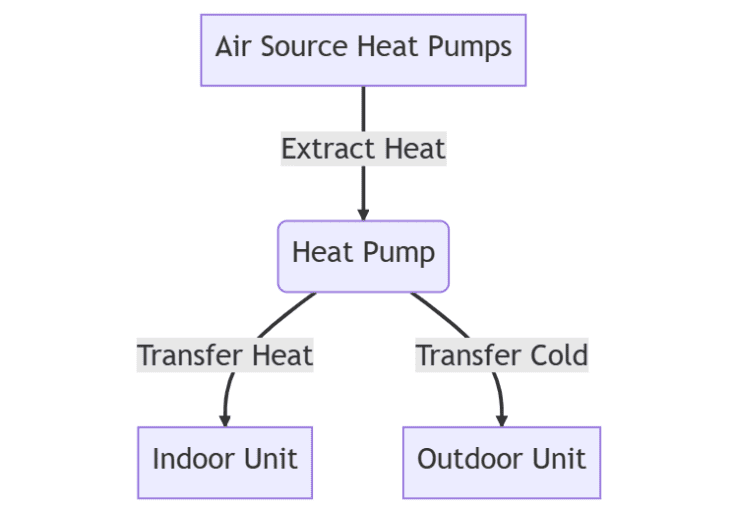
Air source heat pumps are the most common type of heat pump. They work by extracting heat from the outside air and transferring it to the indoor unit.
This heat is then distributed throughout your home via a duct system or through a wall-mounted unit.
One of the main advantages of them is their ease of installation. They do not require any excavation work or ground loops, making them a more cost-effective option.
Air source are also more versatile than other types, as they can be used in a wide range of climates.
Diagram
Ground Source Heat Pumps
Ground source heat pumps are a more expensive option but can be more efficient in certain conditions. They work by extracting heat from the ground via a network of buried pipes, known as a ground loop. This heat is then transferred to the indoor unit, where it is distributed throughout your home.
One of the main advantages of ground source is their efficiency. Since they extract heat from the ground, they can maintain a consistent temperature throughout the year, even in colder climates. As they are also very quiet, as they do not have an outdoor unit.
Water Source Heat Pumps
Water source heat pumps are the most efficient type of heat pump but can also be the most expensive.
They work by extracting heat from a water source, such as a lake or river, and transferring it to the indoor unit. This heat is then distributed throughout your home via a duct system or through a wall-mounted unit.
When combined with a heat pump, solar thermal technology can provide even greater energy savings. A heat pump works by extracting heat from the air or ground and transferring it to your home.
By using the heat from the sun to power the heat pump, you can significantly reduce your energy consumption and carbon footprint.
With solar panels on your roof, you can harness the power of the sun to heat your home, reducing your reliance on traditional heating methods and lowering your energy bills.
One of the main advantages of water source is their efficiency. Since water has a higher heat capacity than air or ground, they can extract more heat with less energy. They are also very quiet, as the outdoor unit is usually located in the water, away from your home.
How Do Heat Pumps Work?
They work by transferring heat from one location to another using a refrigerant. In heating mode, the heat pump extracts heat from the outside air, ground, or water source, and transfers it to the inside of your home. In cooling mode, the process is reversed, and the heat pump removes heat from your home and transfers it outside.
Considerations for Heat Pump Installation
- Size and Capacity: Proper sizing is crucial to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency. A professional installer should assess your space, taking into account factors such as insulation levels, climate conditions, and the heat pump’s specifications, to determine the appropriate size and capacity.
- Installation by Professionals: Heat pump installation requires expertise and knowledge. Hiring a qualified professional ensures that the system is installed correctly, minimizing the risk of performance issues and maximizing its efficiency.
- Regular Maintenance: Routine maintenance is essential for heat pump longevity and efficiency. This includes cleaning or replacing filters, inspecting electrical connections, checking refrigerant levels, and ensuring proper airflow. Following the manufacturer’s maintenance guidelines and scheduling regular service visits is recommended.
- Efficiency Ratings and Features: Consider the efficiency ratings and features of heat pumps when selecting a model. Look for high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) ratings for better energy efficiency. Additionally, features such as variable-speed compressors and smart thermostats can enhance performance and energy savings.
Things to Consider in Heat Pumps
- Energy Efficiency: Look for heat pumps with higher Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) ratings. Opting for more efficient models can result in greater energy savings over time.
- Sizing and Capacity: Properly sizing the heat pump is crucial for optimal performance. An undersized unit may struggle to meet heating or cooling demands, while an oversized unit can lead to inefficient operation and increased energy consumption. Consult with a professional to determine the right size for your space.
- Climate Considerations: Evaluate the heat pump’s performance in your specific climate. Consider the system’s ability to handle extreme temperatures and its coefficient of performance (COP) at different outdoor conditions to ensure it can meet your heating and cooling needs effectively.
- Maintenance Requirements: Understand the maintenance needs of the heat pump, including filter replacements, coil cleaning, and regular inspections. Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule helps maintain efficiency and prolong the system’s lifespan.
Advantages of Heat Pumps
One of the biggest advantages is their energy efficiency. Since they don’t generate heat, they use less energy than traditional heating systems, which can save you money on your energy bills like solar systems. Heat pumps also have a longer lifespan than traditional heating systems and require less maintenance. Additionally, they can be used for both heating and cooling, making them a versatile option.
Disadvantages of Heat Pumps
- Upfront Cost: Heat pumps typically have a higher upfront cost compared to traditional heating and cooling systems. The initial investment can be a significant consideration for some homeowners, although the long-term energy savings can offset this cost over time.
- Climate Dependency: Air-source heat pumps may experience reduced efficiency in extremely cold climates, as the air temperature drops. They might require a supplementary heating source or have to work harder to meet heating demands, potentially impacting their efficiency.
- Installation Complexity: Installing a heat pump requires professional expertise, especially for ground-source or water-source heat pumps. The installation process can be more complex compared to traditional HVAC systems, potentially leading to higher installation costs.
- Space Requirements: Ground-source and water-source heat pumps require sufficient space for the installation of underground loops or access to water bodies. Not all properties may have adequate space or access to meet these requirements.
- Noise: Heat pumps, especially air-source heat pumps, can generate noise during operation. While advancements in technology have reduced noise levels, it’s important to consider the potential impact on occupants or neighbors, particularly in noise-sensitive environments.
Heat Pumps in 2023
In 2023, heat pumps continue to gain traction as sustainable heating and cooling solutions. Advancements in technology have led to improved efficiency, reduced noise levels, and increased reliability. With ongoing efforts to transition to renewable energy sources, heat pumps are expected to play a significant role in achieving energy efficiency goals and reducing carbon emissions.
Conclusion
They are a cost-effective and eco-friendly option for heating and cooling your home. By understanding how they work and the different types available, you can make an informed decision about whether a heat pump is right for your home. I hope that this comprehensive guide has been helpful in your search for information on heat pumps. If you have any further questions, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q: Are heat pumps suitable for all climates?
A: While heat pumps can provide efficient heating and cooling in most climates, extreme cold conditions may impact their performance. Air-source heat pumps might require additional heating methods or defrost cycles to maintain efficiency in colder regions.
Q: Can I use my existing ductwork with a heat pump?
A: In many cases, existing ductwork can be utilized with heat pumps, especially for air-source heat pumps. However, it’s essential to have the ductwork inspected to ensure it is in good condition and properly sized for efficient airflow.
Q: Do heat pumps require backup heating systems?
A: In areas with very low temperatures, it is common to have backup heating systems, such as electric resistance heaters or gas furnaces, to supplement the heat pump during extreme cold spells. This ensures that heating needs are met even in challenging weather conditions.
Q: How long do heat pumps typically last?
A: The lifespan of a heat pump can vary depending on factors such as usage, maintenance, and the quality of the unit. On average, well-maintained heat pumps can last between 15 to 20 years. Regular maintenance and timely repairs can help extend the system
Q: Are heat pumps noisy?
A: Heat pumps have become quieter with advancements in technology. While they do produce some noise during operation, modern heat pumps are designed to minimize sound levels. Choosing models with lower decibel ratings can further reduce noise.
Q: Can I use a heat pump for hot water heating?
A: Yes, heat pumps can be used for hot water heating. Heat pump water heaters are specifically designed to efficiently heat water using the same principles as heat pumps for space heating and cooling.
Q: Do heat pumps require regular maintenance?
A: Yes, regular maintenance is essential for the optimal performance and longevity of heat pumps. This includes cleaning or replacing filters, inspecting components, and checking refrigerant levels. It is recommended to schedule professional maintenance at least once a year.
Q: Are heat pumps eligible for incentives or rebates?
A: Many regions offer incentives, rebates, or tax credits to promote the adoption of energy-efficient heat pumps. These incentives can help offset the initial installation costs and make heat pumps more affordable. Check with local government agencies or utility providers for available programs.