Forms of renewable energy are derived from natural sources that are constantly replenished, making them a clean and sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. From the sun’s rays to the power of the wind, water, biomass, and geothermal heat, all forms of renewable energy have the potential to power our world without harming the environment.
Are you tired of the same old energy sources that harm the environment and deplete finite resources? Are you ready to take a step towards a more sustainable future? Well, you’re not alone! As a society, we’re all looking for ways to reduce our carbon footprint and preserve the planet for future generations. That’s where forms of renewable energy come in.
In this article, we’ll explore all of these forms of renewable energy in detail, so you can gain a deeper understanding of their benefits and potential applications. So sit tight, grab a cup of coffee, and get ready to learn about the exciting world of renewable energy!
1. Solar Power most popular forms of renewable energy
As the world looks for ways to become more eco-friendly, many are turning to renewable forms of energy.
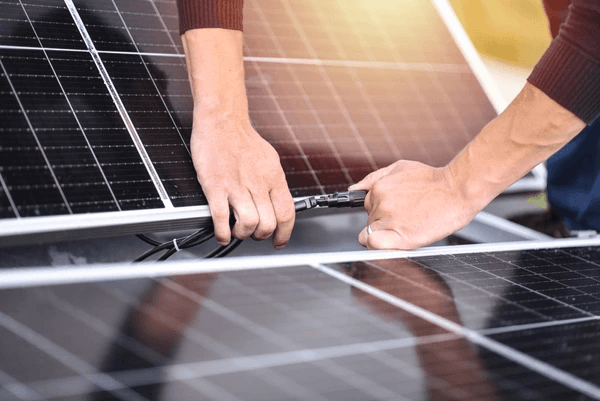
Solar power is one of the most popular forms of renewable energy, and it’s easy to see why. Solar power is a clean and renewable resource that can be used to generate electricity or heat water and air.
Solar power is created when sunlight is converted into electricity. This can be done with solar panels, which are placed in an area where they will receive direct sunlight.
Solar panels are made up of solar cells, which absorb sunlight and convert it into electricity. Solar power can be used to generate electricity for homes, businesses, and even entire communities.
It can also be used to heat water and air or to power solar-powered cars. Solar power is a clean and renewable resource that is becoming more and more popular as the world looks for ways to become more eco-friendly.
2. Wind Power
There are many forms of renewable energy, but few are as ubiquitous as wind power. Wind turbines can be found in fields, on mountaintops, and even in cities.
And while the technology has been around for centuries, it’s only in the last few decades that wind power has become a major source of electricity. In 2018, wind power generated 6 per cent of the world’s electricity, with the United States, China, and Germany being the top three users of wind power.
1. But what is wind power, and how does it work?
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into electricity. Wind energy is created when the sun heats up the earth’s surface, causing hot air to rise and cold air to rush in to replace it. This movement of air creates wind.
2. Wind turbines work by converting the kinetic energy of the wind into electrical energy. The turbine’s blades spin a shaft, which is connected to a generator. The generator then produces electricity.
3. There are two types of wind turbines: horizontal axis and vertical axis. Horizontal-axis turbines are the most common, and they have blades that are perpendicular to the ground. Vertical-axis turbines have blades that are parallel to the ground.
4. Wind power has a number of advantages. It’s a renewable resource, which means it will never run out. It’s also a clean source of energy, as it doesn’t produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants. And it’s a very efficient way to generate electricity.
5. There are also some drawbacks to wind power. The biggest is that it’s intermittent, meaning it only produces electricity when the wind is blowing. This makes it difficult to store wind energy. Additionally, wind turbines can be a visual eyesore, and they can be noisy.
6. Despite these drawbacks, wind power is a promising renewable energy source. With continued research and development, it could play a major role in helping the world transition to a low-carbon future.
3. Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power is a renewable energy source that harnesses the power of moving water to generate electricity.
Hydroelectric power plants use the force of flowing water to turn turbines that drive generators to produce electricity.
Hydroelectric power is a clean and efficient source of electricity that has many advantages over other forms of energy generation.
Hydroelectric power plants do not emit pollutants or greenhouse gases, making them a very attractive option for new power plants. In addition, hydroelectric power is a reliable source of electricity that can provide a constant flow of power even during times of high demand.
The main disadvantage of hydroelectric power is that it requires a large amount of land and water resources.
In order to build a hydroelectric power plant, a dam must be constructed that can hold back a large body of water. In addition, the reservoir created by the dam can displace people that live in the area, as well as disrupt local ecosystems.
Despite the disadvantages of hydroelectric power, it is still a viable option for new power plants due to its many advantages. Hydroelectric power is a renewable energy source that can help meet rising electricity demand without contributing to pollution or climate change.
4. Geothermal Power
Geothermal power is the fifth form of renewable energy on our list. It is also one of the most environmentally friendly, as it produces very little pollution. Geothermal power comes from the heat of the Earth’s core.
This heat is used to generate electricity in a power plant. The plant uses a heat exchanger to convert the heat into steam. The steam then turns into a turbine, which generates electricity. Geothermal power plants can be built anywhere there is geothermal activity.
This activity can be in the form of hot springs, volcanoes, or geysers. The heat from the Earth’s core is harnessed through a process called an enhanced geothermal system (EGS). EGS involves drilling a well into the hot rock, injecting water into the well, and bringing the water back to the surface.
The water is then used to generate electricity in a power plant. EGS is a new technology that is still being developed. It has the potential to be used in many parts of the world, including places that do not have geothermal activity.
Geothermal power is a renewable resource that is environmentally friendly and has the potential to be used worldwide. It is a promising source of renewable energy that should be further explored.
5. Wave and Tidal Power
Wave and tidal power, often called marine energy, refers to the capture of energy from ocean waves, tides, and thermal gradients in the ocean.
Wave energy is a form of renewable energy that has the potential to provide a significant amount of the world’s energy needs.
There are two main types of wave energy: wave power and tide power. Wave power is the energy captured from the motion of waves, while tide power is the energy captured from the rise and fall of tides.
Wave power is a renewable energy resource that has the potential to generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. Wave energy is captured by devices called wave energy converters (WECs), which convert the energy in waves into electricity.
There are two main types of WECs: point absorbers and oscillating water column (OWC) devices. Point absorbers are floating devices that capture energy from the up-and-down motion of waves.
OWC devices are fixed to the seafloor and capture energy from the back-and-forth motion of waves. Wave energy has the potential to provide a significant amount of the world’s electricity needs.
The estimated global resource of wave energy is greater than 2,000 gigawatts (GW), which is equivalent to the electricity generated by all of the world’s nuclear power plants.
The United States has the potential to generate more than 1,200 GW of wave energy, which is enough to power more than 120 million homes. Tidal energy is a renewable energy resource that has the potential to generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases.
Tidal energy is captured by devices called tidal turbines, which convert the energy in tides into electricity. Tidal turbines are similar to wind turbines, but they are submerged in water and capture energy from the tides.
The estimated global resource of tidal energy is more than 800 GW, which is equivalent to the electricity generated by all of the world’s nuclear power plants.
The United States has the potential to generate more than 200 GW of tidal energy, which is enough to power more than 20 million homes. Marine energy has the potential to provide a significant amount of the world’s electricity needs.
Wave and tidal energy are renewable resources that can generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases.
The estimated global resource of marine energy is more than 2,800 GW, which is equivalent to the electricity generated by all of the world’s nuclear power plants.
The United States has the potential to generate more than 1,400 GW of marine energy, which is enough to power more than 140 million homes.
6. Biomass Power
Burning biomass to create power is one of the oldest forms of renewable energy, dating back to the use of wood-burning stoves.
Today, biomass power comes from a variety of sources, including agricultural waste, wood pellets, and even sewage.
Biomass power plant cogs turning While the burning of biomass does release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, it is considered a renewable resource because the plants that are used as fuel will eventually reabsorb the carbon dioxide.
This makes biomass power a carbon-neutral form of energy. There are a few different ways to generate power from biomass.
One is to burn it in a boiler to create steam that can drive a turbine. This is the most common method and is used in many coal-fired power plants that have been converted to run on biomass. Another method is to gasify the biomass, which involves converting it into a gaseous fuel that can be combusted in a gas turbine.
This gas can also be used in a fuel cell to produce electricity. Finally, biomass can be converted into liquid fuels such as ethanol or biodiesel.
These can be used in vehicles or combusted in a boiler to produce power. Biomass power is a versatile renewable energy source that can be used to generate electricity, heat, or liquid fuels. It has the potential to replace a significant portion of the fossil fuels currently being used in the United States.
As the world looks for ways to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels, renewable energy is becoming an increasingly attractive option.
The five most popular forms of renewable energy are solar, wind, water, biomass, and geothermal.
Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, but all offer the potential to generate electricity with far less pollution than fossil fuels.
As technology improves and the costs come down, renewable energy is likely to play an increasingly important role in the world’s energy mix.